
Torsional vibration calculations – marine propulsion
Torsional vibrations are inherent to the operation of internal combustion engines and power transmission systems. In the marine sector, they represent one of the most critical vibratory phenomena affecting the shaft line, the crankshaft and associated components.
An insufficient analysis may lead to excessive stresses, the occurrence of critical speeds within the operating range, or even major failures. Torsional vibration calculations (TVC) are therefore essential from the early design phase of marine propulsion systems.
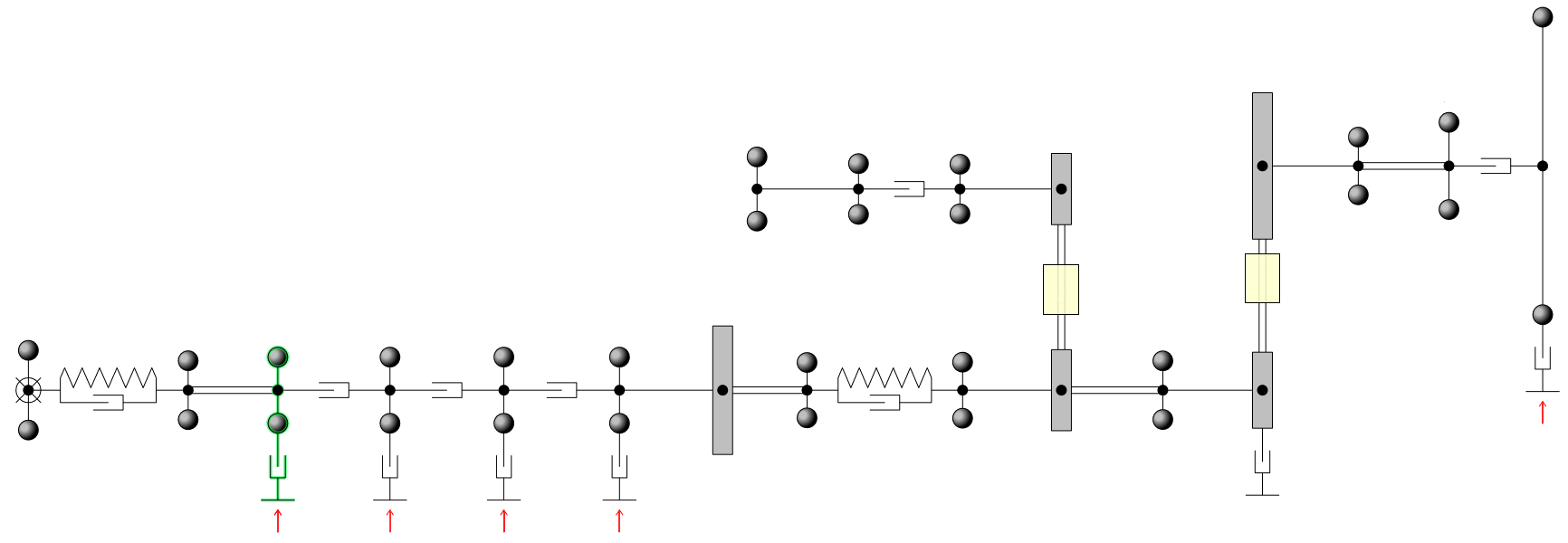
A torsional vibration calculation (TVC) consists in modelling the torsional dynamic behaviour of a power transmission system, from the engine to the propeller.
TVC are essential for marine propulsion
Torsional vibrations are generally the most damaging for propulsion systems. Unlike other vibratory phenomena, they can generate high alternating stresses in shafts and crankshafts, leading to mechanical fatigue. TVC notably allow to:
-
verify compliance with the requirements of classification societies,
-
avoid the occurrence of barred speed ranges within the operating envelope,
-
validate the selection of couplings and damping devices,
-
secure the design before construction, when modifications are still feasible,
-
assess the impact of integrating new equipment into the power transmission line of an existing vessel.
Analysed components
The torsional vibration calculations performed by HEXAMECA cover the entire propulsion system, including:
-
main engine and crankshaft,
-
couplings (rigid or elastic),
-
intermediate shafts and propeller shaft,
-
propeller and associated inertias,
-
optional damping devices.
Calculation methodology
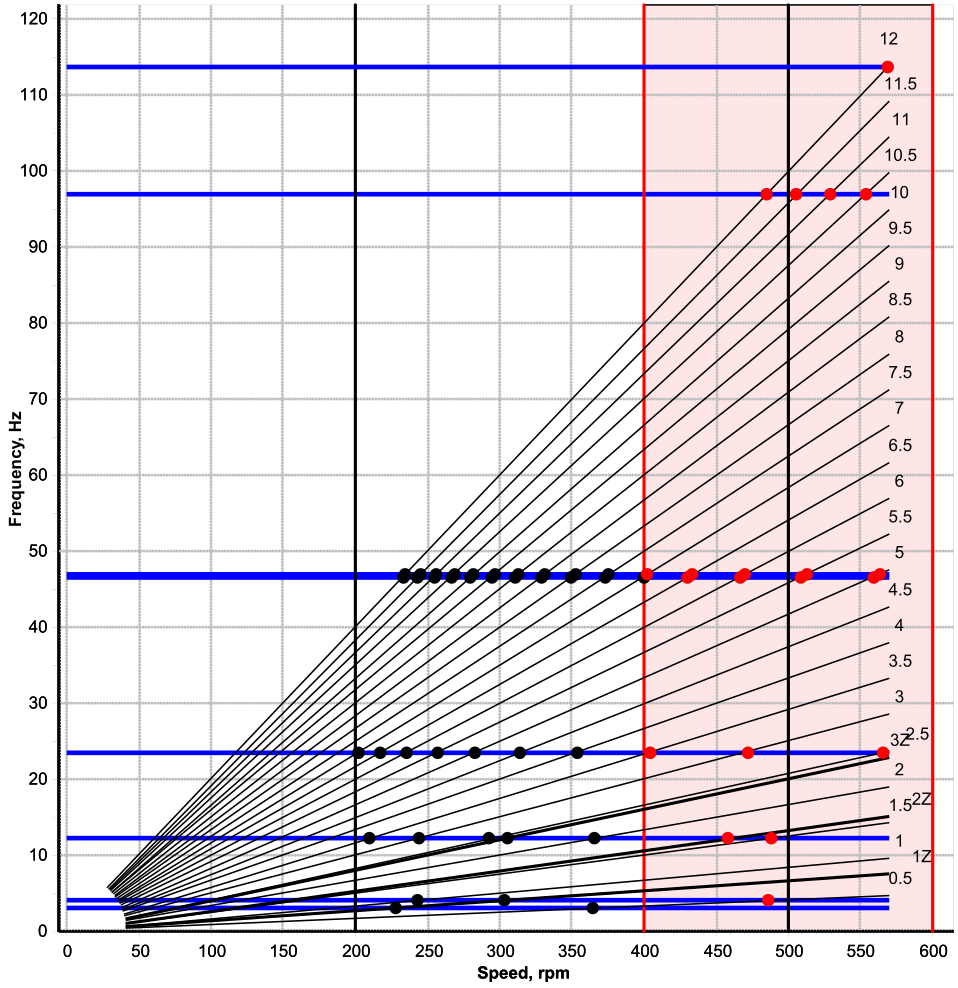
TVC are performed using dedicated numerical models, based on the finite element method applied to rotational dynamics. The methodology generally includes:
-
development of the torsional dynamic model,
-
calculation of natural frequencies and vibration modes,
-
analysis of vibratory responses over the operating range,
-
evaluation of stresses in critical components,
-
identification of potential corrective measures.
The calculations account for variations in stiffness and damping as a function of engine speed.
Results and deliverables
At the end of the study, HEXAMECA provides:
-
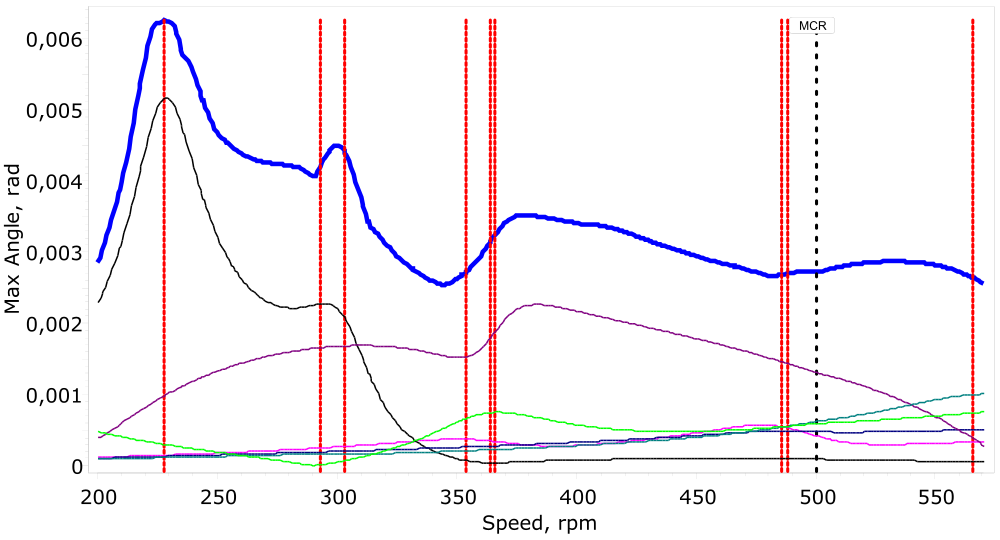
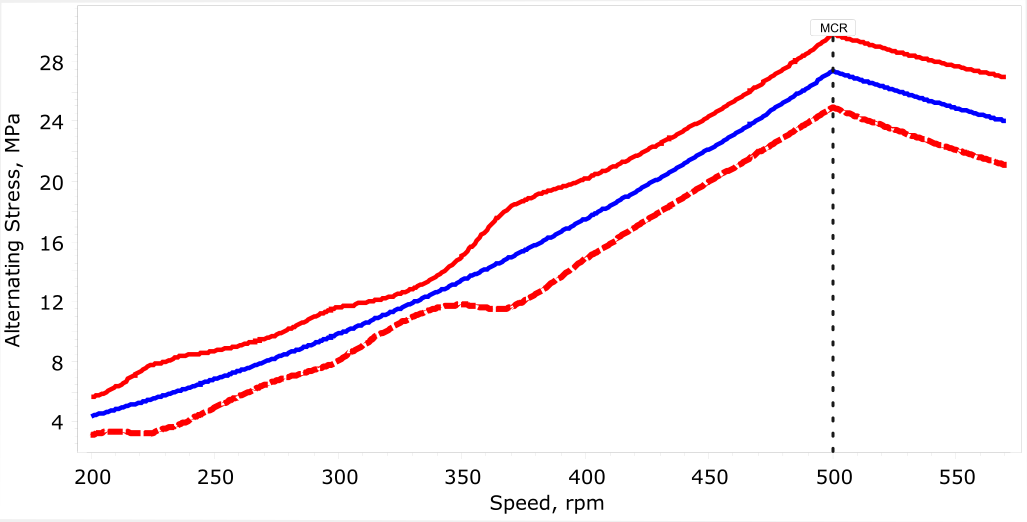
natural frequencies and critical speeds of the system,
-
assessment of vibratory stresses,
-
identification of safe and barred operating ranges,
-
design recommendations (coupling selection, inertia tuning, damper implementation, etc.),
-
documentation suitable for exchanges with classification societies.
Software used
Torsional vibration calculations are performed using ShaftDesigner, a specialised software for the analysis of marine propulsion shaft lines and torsional vibrations.
